Embeddings
Embeddings are numerical representations of text that capture semantic meaning. They are widely used in NLP tasks such as clustering, semantic search, and classification. Shekar provides two main embedding classes with a consistent interface for both words and sentences.
Key Features
- Unified interface: Both classes expose embed() and transform() methods.
- Static and contextual embeddings: Choose between FastText-based static embeddings or ALBERT-based contextual embeddings.
- NumPy-friendly: Directly returns embeddings as NumPy vectors for easy integration.
Word Embeddings
The WordEmbedder class provides static word embeddings using pre-trained FastText models.
Available Models
- fasttext-d100: 100-dimensional CBOW model trained on Persian Wikipedia.
- fasttext-d300: 300-dimensional CBOW model trained on the large-scale Naab dataset.
Note: These embeddings are static and stored as pre-computed vectors for compatibility and stability, since Gensim dependencies are outdated.
Example Usage
from shekar.embeddings import WordEmbedder
# Load the 100-dimensional FastText model
embedder = WordEmbedder(model="fasttext-d100")
# Get embedding for a single word
embedding = embedder("کتاب")
print(embedding.shape) # (100,)
# Find most similar words
similar_words = embedder.most_similar("کتاب", top_n=5)
print(similar_words)
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import arabic_reshaper
from bidi.algorithm import get_display
def fix_persian(text: str) -> str:
return get_display(arabic_reshaper.reshape(text))
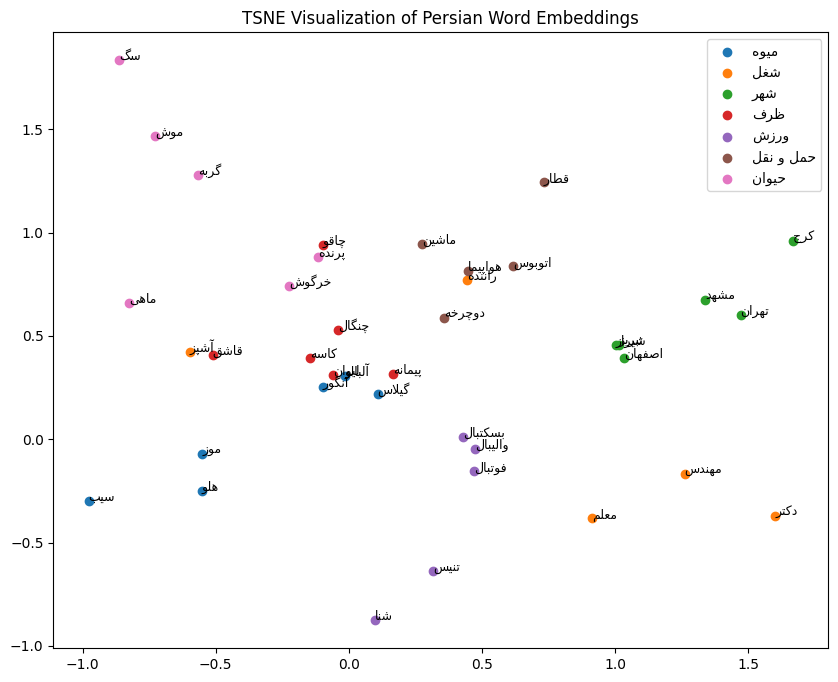
# Categories
categories = {
"میوه": ["سیب", "موز", "انگور", "هلو", "آلبالو", "گیلاس", "توت فرنگی"],
"شغل": ["برنامه نویس", "مهندس", "دکتر", "معلم", "راننده", "آشپز"],
"شهر": ["تهران", "اصفهان", "شیراز", "مشهد", "تبریز", "کرج"],
"ظرف": ["قاشق", "چنگال", "چاقو", "لیوان", "کاسه", "پیمانه"],
"ورزش": ["فوتبال", "بسکتبال", "والیبال", "تنیس", "شنا", "دوچرخه سواری"],
"حمل و نقل": ["ماشین", "اتوبوس", "قطار", "هواپیما", "دوچرخه", "موتور سیکلت"],
"حیوان": ["گربه", "سگ", "پرنده", "ماهی", "خرگوش", "موش"],
}
words, labels = [], []
for cat, items in categories.items():
words.extend(items)
labels.extend([cat] * len(items))
in_vocab_words, in_vocab_labels, embeddings = [], [], []
for word, label in zip(words, labels):
vec = embbeder(word)
if vec is not None:
embeddings.append(vec)
in_vocab_words.append(word)
in_vocab_labels.append(label)
embeddings = np.vstack(embeddings)
tsne = TSNE(n_components=2, random_state=42, init="pca", learning_rate="auto")
embeddings_2d = tsne.fit_transform(embeddings)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
for cat in categories:
idx = [i for i, label in enumerate(in_vocab_labels) if label == cat]
if not idx:
continue
plt.scatter(embeddings_2d[idx, 0], embeddings_2d[idx, 1], label=fix_persian(cat))
for i in idx:
plt.text(
embeddings_2d[i, 0],
embeddings_2d[i, 1],
fix_persian(in_vocab_words[i]),
fontsize=9,
)
plt.legend()
plt.title("TSNE Visualization of Persian Word Embeddings")
plt.show()
Contextual Embeddings
The SentenceEmbedder class uses a fine-tuned ALBERT model trained with Masked Language Modeling (MLM) on the Naab dataset to generate contextual embeddings for entire phrases or sentences.
- Vector Size: 768-dimensional embeddings
- Contextualized: Captures semantic meaning based on surrounding words
Example Usage
